Android Studio Emulator Crashes Mac
Important
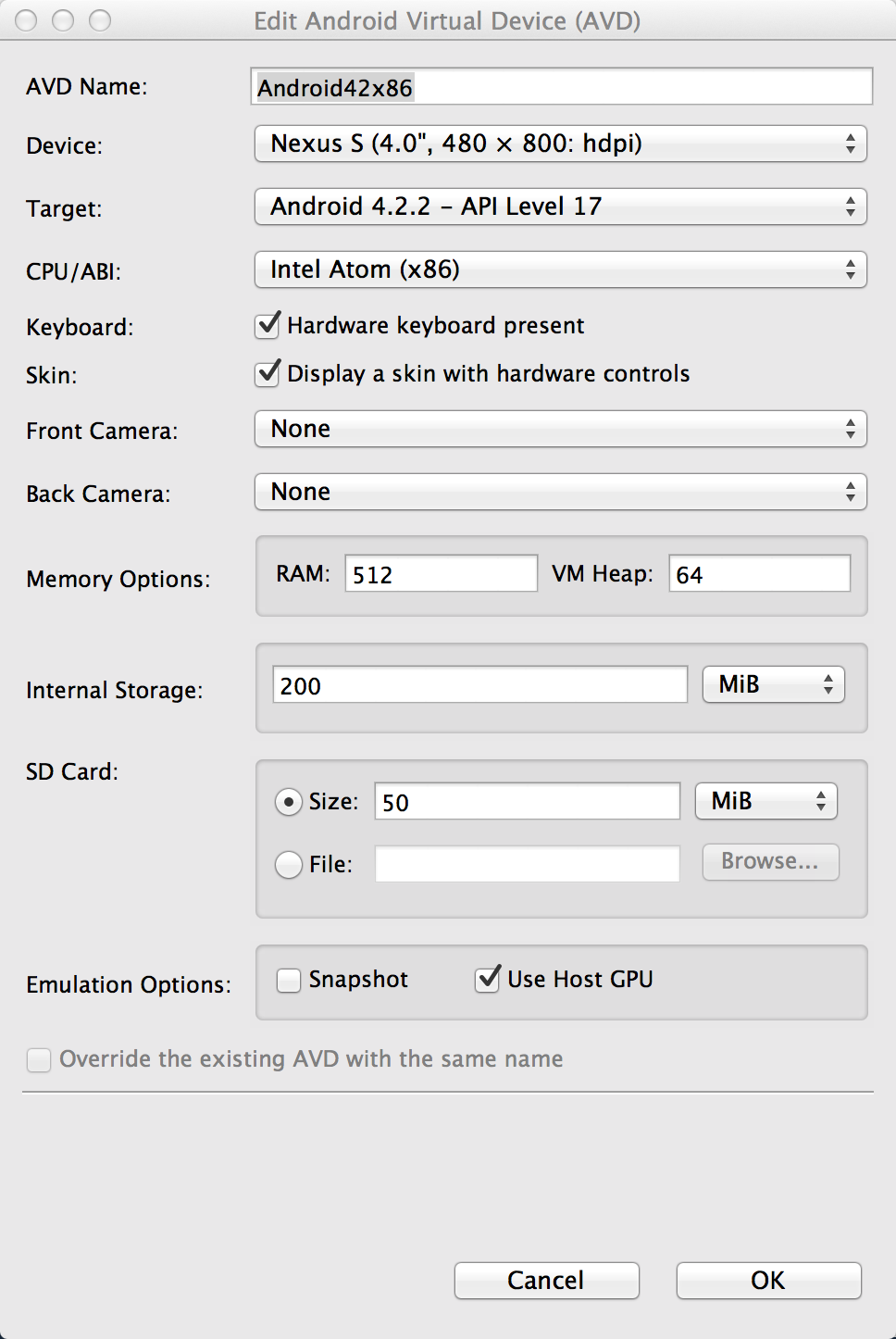
Android Emulator in Visual studio for mac. Visual studio for mac android. Venugopalan Thamotharan reported Aug 10, 2017 at 09:26 AM. Adding language resources w/ wrong region code causes crashes, 'Updating Resources.' Forever, build problems. To start the Android Emulator and run an app in your project: In Android Studio, create an Android Virtual Device (AVD) that the emulator can use to install and run your app. In the toolbar, select the AVD that you want to run your app on from the target device drop-down menu.
This article describes functionality and guidance that is in public preview and may be substantially modified before it's generally available. Microsoft makes no warranties, express or implied, with respect to the information provided here.
Use the Android Emulator with a preview Surface Duo image that is integrated into your development environment to test your app without a physical device. The emulator simulates postures, gestures, hinge angle, mimicking the seam between the two screens, and more. We'll continue to add functionality over time.
The preview Surface Duo image requires that the Android Emulator be installed with Android Studio or Visual Studio (Xamarin).
Note
Read the Xamarin Developers section for help setting up the Surface Duo Emulator to work with Visual Studio.
Run the emulator
After completing the SDK Setup, you can launch the Surface Duo Emulator via the start menu link.
If the emulator does not start, you might need to update the pointer to your Android SDK installation.
- Open the SurfaceDuoEmulator_ version _.dmg file.
- Copy the .jar file and the contents of the emulator folder to your local hard drive. (The emulator folder name cannot have periods in it.)
- If you changed the installation location of the Android SDK from the default, update the pointer to your Android SDK installation.
- In a terminal window, navigate to the folder where you copied the emulator
- Type
./run.shto start the emulator.
- Open the SurfaceDuoEmulator_ version _.deb file.
- Copy the .jar file and the contents of the emulator folder to your local hard drive. (The emulator folder name cannot have periods in it.)
- If you changed the installation location of the Android SDK from the default, update the pointer to your Android SDK installation.
- In a terminal window, navigate to the folder where you copied the emulator
- Type
./run.shto start the emulator.
Update the pointer to your Android SDK
If you changed the installation location of the Android SDK from the default, you will need to update the run script to point to the correct installation location. Otherwise, the emulator will not run when you click the shortcut or run the script.
- Find the installation location of the Surface Duo Emulator. The default location is
%USERPROFILE%SurfaceDuoEmulator. - Open the
artifactsfolder inside of the installation folder. - Make a backup copy of
run.bat- You can copy it to something likerun_androidstudio.bat. - Open the file
run.batin a text editor. - Verify the
ANDROID_SDK_LOCATIONpath value near the top of the file is correct.
- Find the location you extracted the downloaded Surface Duo Emulator archive to.
- Make a backup copy of
run.sh- You can copy it to something likerun_androidstudio.sh. - Open the file
run.shin a text editor. - Verify the
ANDROID_SDK_LOCATIONpath value near the top of the file is correct.
- Find the location you extracted the downloaded Surface Duo Emulator archive to.
- Make a backup copy of
run.sh- You can copy it to something likerun_androidstudio.sh. - Open the file
run.shin a text editor. - Verify the
ANDROID_SDK_LOCATIONpath value near the top of the file is correct.
How to Debug your App on the emulator
Directly in Android Studio
- Open your project in Android Studio.
- Build your project: Build > Make Project or Ctrl+F9.
- Select 'Microsoft SurfaceDuoEmulator API 29' from the list of Running Devices.
- Run your project to deploy it to the emulator: Run > Run 'project name' or Shift+F10.
- To stop debugging: Run > Stop 'project name' or Ctrl+F2.
Using ADB commands
Follow these steps to debug using ADB commands.
Find your emulator device ID
Run
C:>adb devices.Find the package you want to debug.
Run
adb shell pm list packages.Set the app to debug at startup (note the -w)
Run
adb shell am set-debug-app -w com.microsoft.device.display.samples.masterdetail.Start the app in the emulator.
You will get a popup that the app is waiting for a debug to attach. You will need to re-run the set debug each time (or use --persistent option).
Connect Android Studio Debugger
In Android Studio menu options, select Run->Attach debugger. The emulator and process should be listed.
Point to source code and set breakpoints.

Span your app in the emulator
To span your app in the emulator, drag the app from the white bar at the bottom of the app screen towards the middle of the device. When the background turns white across both screens, release the app.
Use the camera
Use this command to list the webcams available on the machine:
~/Android/Sdk/emulator/emulator -webcam-list
If necessary, change the path to match your local installation.
Copy the camera name you want to use, and open the config.ini file. In there you will see something like this:
VirtualBox is a general-purpose full virtualizer for x86 hardware, targeted at server, desktop and embedded use.For a thorough introduction to virtualization and VirtualBox. Perform the following steps to install on a Mac OS X host: Double-click on the dmg file, to mount the contents. A window opens, prompting you to double-click on the VirtualBox.pkg installer file displayed in that window. To install the VirtualBox extension package, do the following: Launch VirtualBox, then click on VirtualBox - Preferences - Extensions in the top bar. Find the blue square with the yellow symbol on the right, and click it. In the file navigator, locate the folder where the extension pack is stored and select it. 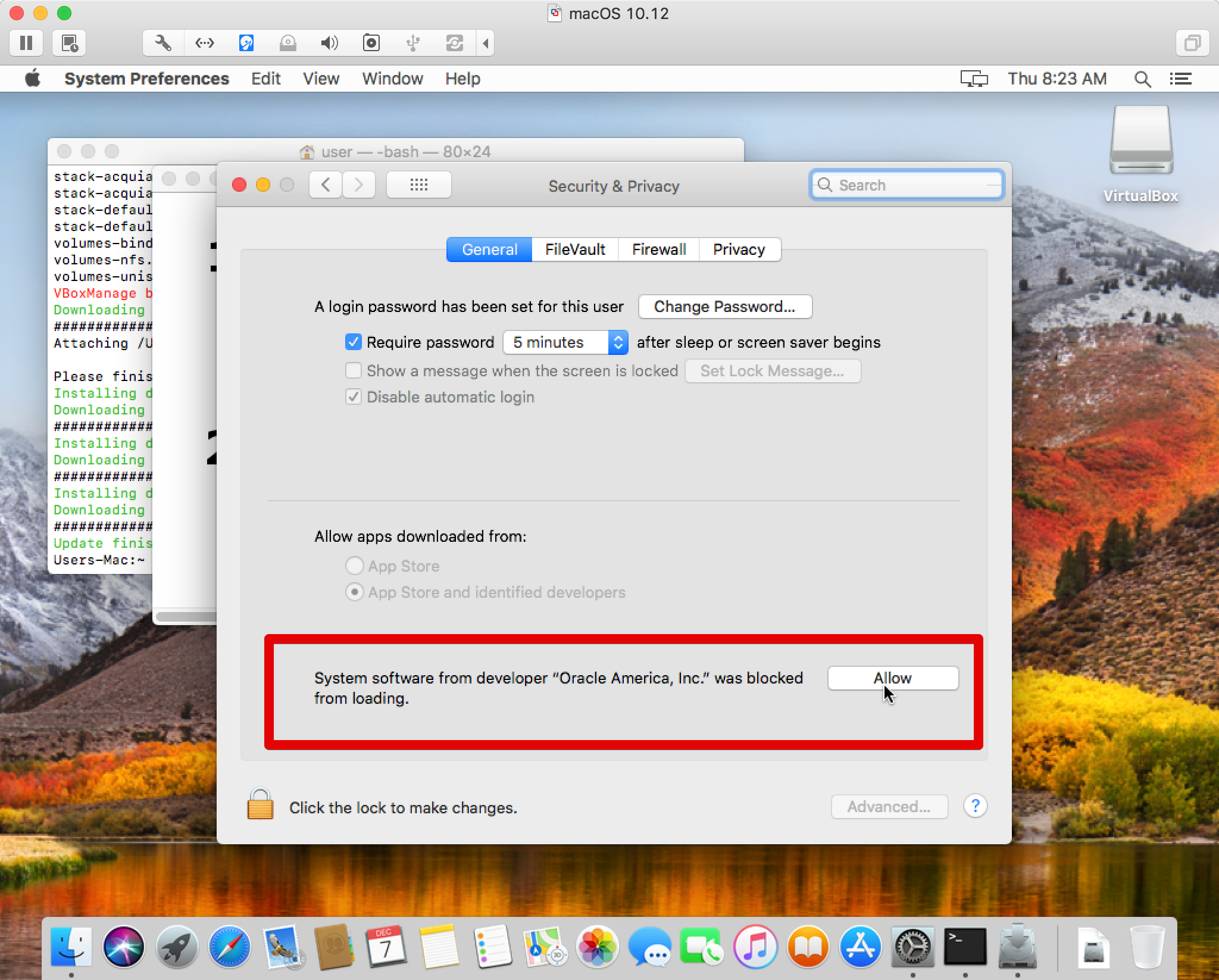
For example, you can change the front camera to use the host machine's webcam.
Xamarin Developers
Important
The preview release of the Surface Duo Emulator requires changes to allow Xamarin Android and Visual Studio to connect to it for deploying and debugging apps.
- Find the installation location of the Surface Duo Emulator. The default location is
%USERPROFILE%SurfaceDuoEmulator. - Open the
artifactsfolder inside of the installation folder. - Make a backup copy of
run.bat- You can copy it to something likerun_androidstudio.bat. - Open the file
run.batin a text editor. - Replace the entire contents of the file with the snippet for your platform below:
- Verify the
ANDROID_SDK_LOCATIONpath value near the top of the file is correct (the default Visual Studio install location is specified).
- Find the location you extracted the downloaded Surface Duo Emulator archive to.
- Make a backup copy of
run.sh- You can copy it to something likerun_androidstudio.sh. - Open the file
run.shin a text editor. - Replace the entire contents of the file with the snippet for your platform below:
- Verify the
ANDROID_SDK_LOCATIONpath value near the top of the file is correct (the default Visual Studio install location is specified).
This section is not applicable to installing the emulator and SDK on Ubuntu or Debian.
Debugging your Xamarin Android App
Open your Project in Visual Studio, build it, and select <build> (Android 10.0 - API 29) (in the list of Running Devices) and deploy.
The name of the emulator in Visual Studio will be fixed in a future release.